General Overview
Oncological diseases of the esophagus include tumors that develop in various parts of the esophagus. These tumors require advanced diagnostic techniques and specialized treatment methods.
Diagnosis and Symptoms
Symptoms of esophageal cancer may include difficulty swallowing, pain in the throat and chest area, weight loss, hoarseness, and difficulty breathing. Diagnosis typically begins with a thorough medical examination, which may include endoscopy, biopsy, CT (computed tomography) scans, and possibly positron emission tomography (PET).
Treatment Methods
The treatment of esophageal cancer involves several approaches:
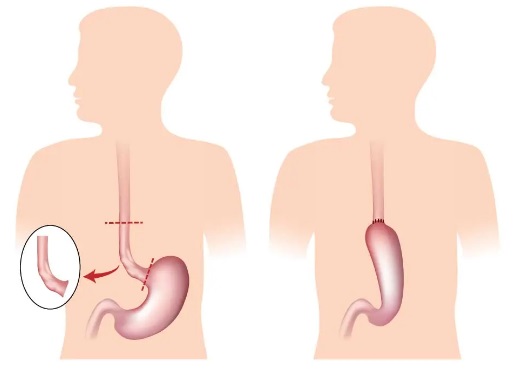
- Surgical Treatment: This may involve partial or total resection of the esophagus. Both minimally invasive and open surgeries can be performed depending on the case.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: These treatments may be used alone or in combination with surgery to halt tumor growth or for additional therapeutic purposes.
- Immunotherapy: In certain cases, immunotherapy may provide effective results and improve the patient’s life expectancy.
Risks and Complications
Complications such as infection, thromboembolism, bleeding, or respiratory issues can arise after surgery. In the long term, patients may experience diarrhea or disturbances in gastrointestinal microflora.
Rehabilitation and Aftercare Support
After surgery, patients often require the support of a nutritionist, psychologist, and physical therapist. Rehabilitation will vary depending on the type and extent of the surgery.